NSE Buzz: Tracking the Giants of the Indian Market
The National Stock Exchange of India is the backbone of India’s stock market, helping businesses raise money and giving individuals a chance to grow their wealth. Recently, there's been significant buzz surrounding the anticipated issue offering, which has notably impacted the price of NSE Unlisted Shares trading at [View NSE Unlisted share price today]
Imagine you have some extra money saved, but it’s sitting in your bank account earning very little interest. Meanwhile, some businesses need money to expand, hire more people, or launch new products. The stock exchange acts as a marketplace that brings together people who have money to invest with companies that need funds. The buzz in the pre-IPO price has drawn investors towards the NSE share price in grey market.
What is NSE and How Does it Operate?
The NSE was established in 1992 and became fully operational in 1994. Before this, stock trading in India was largely unstructured and lacked transparency. Prices were often manipulated, and access to markets was limited to a few privileged players. NSE changed the game by introducing an electronic trading system, making the process faster, fairer, and more accessible to everyone.
Today, it is one of the world’s largest stock exchanges by trading volume. It offers a variety of financial products, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives, allowing investors to participate in different types of investments based on their risk appetite. The exchange operates on a framework that ensures transparency, efficiency, and investor protection.
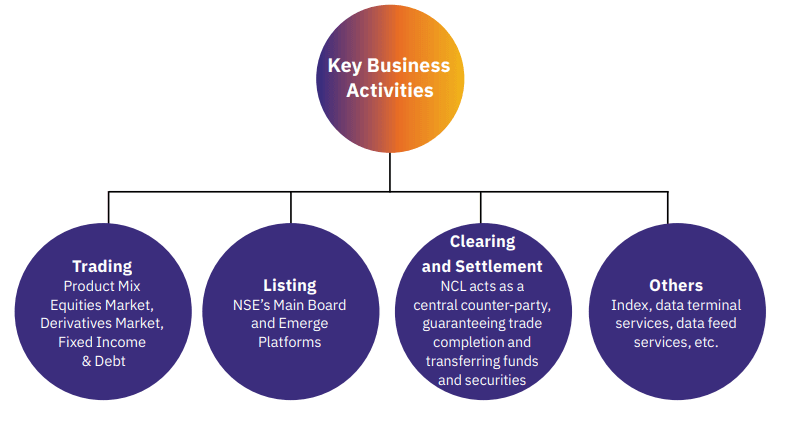
It operates through a highly efficient and fully automated trading system. Here’s how it functions:
Order Matching System – The exchange uses a fully automated system to match buy and sell orders in real time. When an investor places a buy or sell order, it is processed through an electronic system that ensures fair pricing based on supply and demand. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and ensures that orders are executed swiftly and accurately.
Clearing and Settlement – Once a trade is executed, it needs to be settled. The NSE, through its subsidiary, National Securities Clearing Corporation Limited (NSCCL), ensures that securities and money are transferred smoothly between buyers and sellers. The settlement cycle follows the T+1 mechanism, meaning trades are settled within one business day, reducing risk and improving liquidity in the market. Clearing houses ensure that transactions are honored, eliminating the risk of counterparty default and bringing stability to the trading system.
Market Segments – It is not just about stocks. It offers trading in multiple segments:
Equity Market → This is where shares of companies are bought and sold. When a share is owned, it represents a small part of the company. If the company performs well, the share value increases, and if the company faces challenges, the value may decrease.
Derivatives Market → This market involves contracts based on the future price of assets like stocks, indices, or commodities. It’s like agreeing today on what something will cost in the future. These contracts help manage risks from price changes or enable profit from predicted price movements. For example, a farmer may lock in a price for crops to avoid losses if market prices drop later.
Debt Market → In this market, instead of selling ownership (like shares), companies and governments raise money by issuing bonds. When bonds are purchased, money is lent to the issuer, who promises to pay it back with interest over time. This provides a more stable return compared to stocks.
Currency & Commodity Market → This is where currencies (like dollars or euros) and raw materials (such as gold, oil, or wheat) are traded. Businesses use this market to secure prices and protect against sudden price changes that could impact profitability.
Mutual Funds & ETFs → These are baskets of various investments (stocks, bonds, or commodities) managed by experts. Instead of selecting individual investments, a ready-made mix is chosen, which helps reduce risk by diversifying across different assets.

1. Trading Services (80.54% of Revenue)
This is the main way NSE earns money. When people buy or sell stocks or other financial products on the exchange, it charges a small fee for every trade. The more people trade, the more money they make. So, buying and selling is the biggest money-maker for the exchange.
2. Colocation Charges (5.91% of Revenue)
Colocation is when traders set up their computers inside the NSE building. This helps them trade faster because their computers are very close to the system. Traders pay for this speed advantage, especially those who need to make fast trades.
3. Exchange Listing (1.49% of Revenue)
When companies want to list their shares on the NSE (so people can buy and sell them), they have to pay fees. This is a small part of their income but helps bring more companies to the exchange and build credibility.
4. Other Services (12.06% of Revenue)
This includes other ways NSE makes money:
- Selling market data: The exchange shares information about the market, and traders pay for it.
- Clearing and settling trades: They charge for helping finalize trades between buyers and sellers.
- Licensing services: Companies pay to use their financial data and tools.
1. Infrastructural Advantage
High-Speed Trading Platforms: NSE operates one of the fastest and most efficient trading systems globally. This system executes transactions in milliseconds, which means that buy and sell orders are completed quickly. The speed reduces the impact of price volatility that can occur when orders are delayed, ensuring a smoother market environment. This speed benefits both institutional and retail investors by giving them access to a fair and rapid trading experience.
Algorithmic Trading: Institutional investors often use automated systems, or algorithms, to trade stocks based on pre-set strategies. These systems can place large orders in fractions of a second, improving liquidity by making it easier to buy and sell large amounts of stock without disrupting the market. This also improves efficiency, as orders are executed more quickly and at optimal prices.
2. Regulatory Framework and Investor Protection
A strong regulatory system helps build trust, ensuring a fair and secure environment for trading.
SEBI Oversight: The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) plays a pivotal role in regulating the NSE. SEBI ensures that the exchange operates according to strict rules and regulations, preventing market manipulation and fraud. This oversight builds investor confidence, knowing that the market is being closely monitored and regulated to maintain fairness.
Investor Protection Fund (IPF): In case of a broker default, the NSE has an Investor Protection Fund to compensate investors for their losses. This fund acts as a safety net, providing protection for retail investors and ensuring that their financial interests are safeguarded even if a broker fails to meet its obligations.
3. Growing Retail Participation and Financial Awareness
Stock market investing, once limited to institutional players, is now being embraced by a growing number of retail investors.
Digital Investment Platforms: With the rise of mobile apps and online trading platforms, retail investors can now trade in stocks easily, often from their smartphones. These platforms are user-friendly, making it simpler for individuals with little or no prior experience to enter the stock market. The convenience and accessibility of digital platforms have led to an increase in retail investor participation in the stock market.
Education and Awareness: Financial literacy has grown in recent years, with more people learning about investing through social media, financial blogs, and educational campaigns. As financial knowledge increases, more people are feeling confident enough to invest in the stock market. This shift is empowering individuals to make informed investment decisions, ultimately leading to higher participation in the market.
Better Returns Compared to Traditional Savings: With interest rates on traditional savings accounts remaining low, many people are seeking alternative ways to grow their wealth. The stock market offers higher potential returns over the long term, making it an attractive option for those looking to increase their savings. As a result, more individuals are choosing to invest in equities and mutual funds, leading to increased retail participation.
4. India’s Economic Growth and Policy Reforms
India’s strong economic growth and supportive government policies are key factors driving the growth of the NSE.
Rising GDP and Corporate Earnings: India’s rapidly growing economy leads to higher corporate earnings, which in turn attract more investment in the stock market. As businesses expand and profits increase, the stock prices of these companies generally rise, making them more attractive to investors. This growth in corporate profits is a direct result of the expanding economy and is a strong indicator of future market potential.
Government Incentives and Reforms: The Indian government has implemented a series of policies aimed at boosting the stock market. These include promoting digital banking, encouraging startup IPOs, and attracting foreign investment into the country. These policies have made the Indian stock market more appealing to both domestic and international investors, increasing participation.
Expanding Middle-Class Wealth: As India’s middle class grows, so does its disposable income. A wealthier middle class is more likely to invest in the stock market, seeking to build long-term wealth. The rise in disposable income is fueling investments in both stocks and mutual funds, as individuals have more funds available for investment. This trend is contributing to the increasing retail participation in the NSE and driving further growth.
Competitive Positioning and Market Standing
The National Stock Exchange of India has the highest turnover, which refers to the total value of buying and selling activity on the exchange within a given period, being the highest among peer exchanges in India due to its dominant 93% market share in the equity cash segment, supported by its technology and ability to execute large volumes of transactions, investor base, greater liquidity, and strong network effects. The NSE Pre IPO price is henceforth greatly influenced by its competitive standing among peer exchanges like BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) or Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India (MSEI).

Market Leadership: Being the premier stock exchange in India, it plays a pivotal role in shaping the country's financial standpoint. The NSE is the largest derivatives exchange in the world for the fifth consecutive year, based on the number of contracts traded. Furthermore, it is the largest exchange in the world in terms of the number of trades per day, processing over 2,000 crore orders and over 29 crore trades on some days.
Investor Base: There is a significant increase in its investor base, with the number of unique registered investors tripling in the last four years to 9.2 crores by March 2024. The number of investors increased from 8 crore to 9 crore in just five months.
Capital Formation: The NSE plays a crucial role in capital formation by efficiently allocating capital to enterprises, including both traditional and new-age companies. It offers a wide variety of financial products, enabling different types of companies, such as social enterprises and MSMEs, to raise capital. In FY 2023-24, 213 new companies were listed on the NSE. The exchange listing helps companies raise capital, improve visibility, and enhance liquidity.
Key Headwinds Facing the Indian Capital Markets
While India’s capital markets have made major strides, there are several emerging challenges that could slow down their progress. The following factors stand out as critical potential headwinds:
Geopolitical Instability and Global Trade DisruptionsThe rise of geopolitical tensions and protectionist policies globally can have a domino effect on emerging markets like India. This could lead to capital outflows, disrupt global supply chains, and harm the profitability of Indian companies that depend on international markets, causing investor sentiment to fluctuate.
Structural Bottlenecks in Financial InfrastructureAlthough technology has driven growth, gaps in market infrastructure—such as scalability challenges for high-volume trading and lack of interoperability across platforms—can limit the full potential of the market. Improving trading speed and enhancing resilience during market fluctuations is critical to prevent operational disruptions and ensure smooth market functioning.
Dependence on Derivatives Market for RevenueThe NSE generates the majority of its revenue from the derivatives market, but its reliance on this volatile segment exposes the exchange to greater risk. Regulatory measures by SEBI, such as the six-step plan to increase entry barriers for retail investors, aim to curb mounting retail investor losses. This has been seen to potentially reduce F&O (Futures and Options) trading volumes by up to 40%, impacting the overall revenue model of the exchange.
Challenges in Expanding Retail Participation in Complex Asset ClassesWhile retail investor participation has increased, the adoption of more complex products like municipal bonds, green bonds, and real estate investment trusts remains slow. Despite efforts to boost financial literacy, many retail investors still lack confidence in these newer asset classes, limiting the market’s potential for diversification and growth.
Financial Standpoint of NSE
1. Profitability and Turnover
The NSE has shown year-on-year 28% revenue growth to ₹16,433.61 crores in FY 23-24, driven by increased trading volumes, particularly in the cash market and equity futures and options segments, higher transaction charges, and growth in data center and connectivity charges. The average daily turnover in the cash market increased by approximately 53%, and in the equity F&O segment by around 21%. The profit after tax reached ₹8,305.74 crores, a 12.91% increase compared to the previous year. The operating margin stands at 71%, which indicates that it is not only generating more revenue but is also effectively converting this into profit. This profitability is the primary factor driving the recent surge in the NSE share price in unlisted market.

2. Operational Highlights
- Settlement and Clearing: The National Stock Exchange has made the process faster by switching to a T+1 system. This means that when you buy or sell stocks, the trade is completed within one business day, so shares are delivered to you quicker. There’s also an option for even faster transactions with the T+0 system, which lets you complete trades almost immediately.
- Market Reach and Expansion: The NSE is becoming more accessible to people around the world. For example, the NSE International Exchange, located in Gujarat’s GIFT City, saw a huge rise in trading activity, with daily trading nearly tripling in 2024. Additionally, the exchange is helping more small businesses get listed on the stock market, under the small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) segment.
- Capital Raising: In FY 2024, the exchange helped raise ₹13.8 lakh crores through stock and bond listings. This shows how important the exchange is in supporting businesses to raise funds. They also launched a new Social Stock Exchange, where social organizations can raise money.
- Technology and Infrastructure: The NSE continues to invest in improving its technology. It spent ₹1,095 crores on upgrading its systems. For example, it now uses a new data system that can process over 500,000 orders every second, making transactions faster and more reliable. The exchange also has a solid technical infrastructure, including data centers, more servers, and a huge amount of data storage to support its operations.
The National Stock Exchange of India has transformed the way Indians invest, making financial markets more accessible, transparent, and efficient. Its commitment to technology, regulatory compliance, and investor protection has positioned it as a powerhouse in the financial markets. As India continues its journey of economic growth and digital transformation, the NSE will play an even more crucial role in wealth creation and financial inclusion, which makes the upcoming IPO an important event to keep an eye on, as it will shape the scope of the NSE grey market price.