Analyzing Cochin International Airport: Trends in Share Prices and Unlisted Shares
The Indian aviation sector is showing growth, driven by rising passenger traffic, strategic public–private partnerships, rapid innovations, and a strong focus on sustainability. Among the key players in this sector, Cochin International Airport Limited (CIAL) which stands out for its unique public-private partnership model, rapid growth in air traffic and retail segment, and innovative approaches to handling emerging market demands. While the airport has long been recognized for its green energy initiatives and infrastructure upgrades, there’s growing buzz around the Cochin International Airport unlisted share price [View Here]
The aviation industry plays a crucial role in global connectivity, trade, and tourism, and is made up of various interconnected elements such as aircraft manufacturers, airlines, and airport operators. The Indian aviation market is currently the third-largest globally and is continuing to experience growth driven by a variety of factors, including increasing passenger traffic, strategic investments and government support. The aviation sector significantly contributes to the GDP and offers various opportunities in areas like maintenance, repair, and overhaul, with India aiming to become a global hub.
Cochin International Airport Share Price: Market Performance & Insights
- Passenger Traffic: In FY 2024, India saw 376.43 million air passengers, indicating a continued upward trend. This positions India as a major player in the global aviation industry.
- National Monetisation Pipeline: The government is increasing investments in the aviation sector through initiatives like the National Monetisation Pipeline. This initiative aims to leverage private sector participation to modernise and expand airport infrastructure.
- Digi Yatra: The Digi Yatra initiative uses facial recognition technology to provide a seamless and hassle-free experience for passengers at airports, which has seen adoption with over 4.58 million users. This digital framework enhances passenger throughput through existing infrastructure.
The Potential of Cochin International Airport Unlisted Share Price
CIAL’s operations encompass a wide range of activities, from handling passenger and aircraft movements to managing extensive infrastructure projects. These operations are critical to the airport’s ability to serve as a major hub in South India and drive economic activity in the region.
Passenger and Aircraft HandlingCIAL has achieved milestones in passenger handling, which involves all processes related to the efficient movement of travelers through the airport—from check-in and security screening to boarding and deplaning. In FY 2023–24, the airport handled 10.52 million passengers. Moreover, the airport recorded its highest ever air traffic movement, with 70,203 flights operating through its terminals.
Infrastructure and Expansion ProjectsInfrastructure is the backbone of any major airport. CIAL has invested heavily in the development and expansion of its facilities to accommodate future growth. Several key projects are currently underway, including:
- The completion of the Import Cargo Complex, which is a new facility that is like a dedicated warehouse for handling incoming shipments from other countries. It makes it easier and faster to unload, store, and clear goods through customs. By improving these processes, the airport can move freight more quickly and efficiently, which in turn helps boost revenue from cargo services.
- Seven mega projects that include the development of transit accommodations which are the rest areas for travelers, the construction of a star hotel, and the expansion of the international terminal. These initiatives aim to improve passenger amenities and enhance the overall travel experience.
- The implementation of advanced digital solutions such as the Digi Yatra system, which simplifies the check-in process and reduces passenger waiting times by automating various functions.
- Setting up a 50 MW solar power plant and a 12 MW project in Payyannur helps cut costs and shows their dedication to green energy. These projects keep the airport strong as more passengers and cargo move through
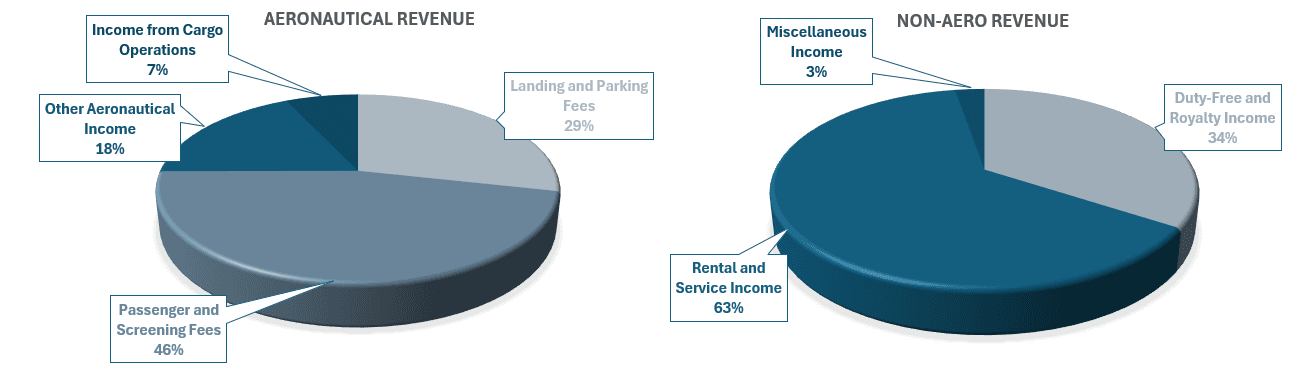
CIAL’s revenue model is multifaceted, consisting of both aeronautical and non-aeronautical components. Each stream is critical in ensuring the airport’s financial stability and growth, all of which can highly affect Cochin International Airport’s unlisted share price.
Aeronautical Revenue
Aeronautical revenue is generated directly from the core services provided to airlines and passengers. It comprises several specific charges and fees, each playing a distinct role in the airport’s income:

Landing FeesLanding fees are charges levied by the airport authority on airlines whenever an aircraft lands at the airport. These fees are designed to cover the costs of maintaining critical infrastructure, particularly the runway system, taxiways, and airfield lighting. These fees also help in the upkeep of other vital operational areas, such as the air traffic control system and the maintenance of ground support equipment.
User Development Fees (UDF)User Development Fees (UDF) are charged as part of the passenger’s ticket price. These fees are earmarked specifically for funding infrastructure development projects at the airport. UDF helps airports finance significant improvements and expansions like terminal upgrades, runway extensions, or building new facilities to accommodate growing passenger numbers.
Parking and Housing FeesParking and housing fees are levied on airlines that park their aircraft at the airport’s designated areas, such as aircraft parking stands. While this revenue stream might be smaller compared to landing fees, it still contributes greatly to the airport's aeronautical revenue. These fees are necessary to maintain the parking facilities, provide security, and offer support services like fuel supply, maintenance, and aircraft ground handling.
Aerobridge ChargesAerobridge charges apply when airlines utilize the aerobridges connecting the terminal to the aircraft. These bridges are important for ensuring smooth passenger boarding and disembarkation, particularly for larger aircraft. Aerobridge charges are designed to recover the costs of installing, operating, and maintaining the bridges, which enhance passenger convenience and speed up the boarding process.
Passenger Service Fees and CUTE ChargesPassenger Service Fees (PSF) are levied to cover various services provided to passengers during their stay at the airport, such as seating, toilets, security checks, and airport lounges. These fees are typically collected as part of the airline ticket purchase or added to the passenger’s total airport-related costs.
In addition, Common User Terminal Equipment (CUTE) charges refer to fees related to shared terminal facilities like baggage screening systems, check-in counters, and other common infrastructure used by multiple airlines. The CUTE system allows airlines to share infrastructure and equipment, making operations more cost-efficient.
Inline X-Ray Screening Charges and RoyaltiesCargo operations form a critical part of the airport’s overall business model, contributing significantly to revenue. Revenue from cargo operations arises from the handling, storage, and transportation of goods, both domestic and international. As global trade continues to expand, efficient cargo handling becomes more important, and airports need specialized infrastructure, such as cargo terminals, refrigerated storage, and handling equipment.
For the airport, its ability to handle cargo, particularly perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and e-commerce shipments, adds valuable revenue, with freight services becoming a more profitable segment. In FY 2023–24, CIAL generated Rs. 43.4 crores from cargo operations, reflecting the importance of this sector to the airport’s overall revenue structure.
Cargo OperationsCargo operations form a major part of their business model. In the FY 2023–24, revenue from cargo operations amounted to Rs. 43.4 crores. Cargo operations include the handling, storage, and transportation of goods—activities that require specialized facilities and expertise. As global trade expands, the ability to efficiently manage cargo becomes increasingly important, contributing not only to the airport’s overall revenue but also to the regional economy.
Together, these streams form a regulated and reliable source of income for CIAL, as tariffs are determined by the Airport Economic Regulatory Authority of India (AERA). This regulatory oversight ensures a balance between profitability and service affordability.
Non-Aeronautical Revenue
Non-aeronautical revenue comprises income from activities not directly related to flight operations. This diversification is crucial for reducing dependence on aeronautical charges, particularly during periods of fluctuating passenger traffic.

Duty-Free and Retail OperationsDuty-free shops and retail stores inside the airport generate a large portion of income that is not directly related to flight operations. These stores sell products like perfumes, electronics, chocolates, and liquor at tax-free prices, making them attractive to travelers. In the financial year, duty-free sales alone brought in Rs. 112.95 crores in revenue. Since passengers often shop while waiting for their flights, this business remains a key source of profit for the airport, helping to support overall operations and future expansions.
Rent and ServicesThe airport earns income from renting out commercial spaces, office facilities, and retail outlets within its premises. In FY 2023–24, rent and services contributed Rs. 208.58 crores, reflecting the value of the airport’s real estate and facilities management capabilities.
Trade Fair Centres, Golf Courses, and Related FacilitiesIt also operates specialized venues such as trade fair centres and golf courses. Income from these facilities is generated through event hosting, membership fees, and other related services. These streams are essential in boosting non-aeronautical revenue and diversifying the airport’s financial profile.
Other Ancillary ServicesApart from flights and duty-free sales, the airport also earns from advertising, parking fees, restaurants, and entry charges for special areas or events. These services bring in consistent income and support overall airport operations, making the business more stable and less dependent on airline-related earnings.
Investing in Cochin International Airport Unlisted Shares: What You Should Know
The sustained growth of Cochin International Airport is underpinned by several key drivers that span demographic trends, government policies, technological innovations, and strategic initiatives. Understanding these growth drivers provides insight into the airport’s long-term potential.
Expanding Passenger Demographics and Market PotentialAs more people enter the middle-income bracket, disposable incomes rise, making air travel more accessible. This demographic shift translates directly into increased passenger numbers for CIAL. Higher passenger traffic not only boosts aeronautical revenue through increased landing fees and user development fees but also drives non-aeronautical revenue from retail, food services, and parking. In essence, a larger pool of travelers creates a ripple effect that benefits nearly every aspect of the airport’s operations.
Government Policies and Support for Aviation InfrastructurePolicies that support regional connectivity, airport modernization, and the development of public–private partnerships have provided the necessary regulatory and financial backing for ambitious projects. For example, the government’s efforts to develop these models for airport operations have attracted private sector investment, increasing the airport’s capacity and service quality. These policies are instrumental in creating an enabling environment that fosters sustained growth and innovation in the aviation industry.
Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs)CIAL’s operational model is a prime example of successful collaboration between the public and private sectors. By leveraging the strengths of both domains, the airport is able to offer world-class services while ensuring efficient management and rapid expansion. The PPP model has not only helped in mobilizing capital for infrastructure projects but also in transferring technical expertise, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and service quality.
Technology as a BoonTechnology is helping the aviation industry work more efficiently. AI systems are used to manage air traffic, and IoT (which means connecting devices to the internet) helps track things like baggage, equipment, and even the weather in real-time. Digital tools like Digi Yatra also make travel smoother. These improvements help airports handle flights faster, use resources better, and keep safety high, all of which are important for staying competitive in a fast-changing industry.
Enhanced Passenger Experience and Value-Added ServicesImproving passenger services, such as faster check-ins, smoother security, and better shopping and leisure options, directly impacts passenger satisfaction and loyalty. By focusing on enhancing the travel experience and offering more than just flights, like premium dining and lounge access, airports can grow and remain competitive in the long run.
Competitive Positioning and Future Outlook

Strategic Vision and Long-Term PlanningCochin International Airport is more than a travel hub. Its long-term vision goes beyond traditional operations by transforming itself into a dynamic, sustainable, and technology-driven ecosystem. The airport is investing in modern infrastructure, embracing digital initiatives like face recognition and streamlined check-ins, and expanding into non-aviation areas. This forward-thinking approach not only improves day-to-day operations but also sets the stage for future growth and roadmap.
India’s First Greenfield Airport Built Through Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
As India’s first greenfield airport developed entirely through a public-private partnership, Cochin International Airport redefined how major infrastructure projects can be financed and managed. This pioneering model has since become a benchmark for new airport developments across the country.
Focus on Regional ConnectivityRecognizing the unique needs of its community, CIAL is actively working to boost regional connectivity. It is planning to launch a low-cost airline, Air Kerala International Services, to serve the large population of non-resident Keralites. In addition, the airport is developing a golf resort that will provide travelers with a seamless blend of leisure and transit services, enriching the overall travel experience.
Market Leadership in South IndiaCIAL’s innovative strategies and continuous improvements have established its leadership in South India. It stands out as the only airport in Kerala and one of just four in South India to handle more than one crore passengers annually. This solid performance, driven by a commitment to sustainability, digital transformation, and customer service, positions the airport for continued long-term growth and profitability.
Financial Standing of CIAL
CIAL’s financial performance is a key indicator of its operational success and strategic positioning within the aviation industry. The airport’s revenue generation, profitability, and prudent capital management underscore its ability to deliver long-term value to its stakeholders.

Record Revenue and ProfitabilityIn the FY 2023–24, CIAL achieved a record gross income of Rs. 1,014 crores—its highest annual revenue to date. This figure represents a 31.53% increase in revenue compared to the previous year, reflecting the rapid expansion in both passenger and cargo operations. Such record-setting financial performance is attributable to strategic investments in infrastructure, enhanced operational efficiency, and the successful integration of non-aero revenue streams, that is, the collection of user development fees, royalty from duty free sales, and an increase in aeronautical tariffs.
The Profit after tax also increased as a result from Rs. 267.17 crores to Rs. 412.58 crores over the same period. These figures illustrate the impact of the airport’s expansion and revenue enhancement strategies on overall profitability.
Borrowings and Capital ManagementCIAL’s financial strategy is built on a balanced mix of equity, internal accruals, and borrowings. During FY 2022–23, the company successfully issued Right Shares to its existing shareholders in a ratio of 1:4, raising Rs. 564 crores. This infusion of capital was used to fund key projects and maintain liquidity. The prudent use of borrowings, both long-term and short-term, ensures that the airport can invest in infrastructure without putting its financial stability at stake and shows increased investor confidence.
Current RatioThe current ratio increased from 2.98x to 3.48x, indicating an enhanced capacity to meet short-term obligations. A higher current ratio is generally seen as a positive sign, reflecting strong liquidity.
Debt-Equity RatioThe debt-equity ratio declined from 0.38x to 0.22x, demonstrating a reduced reliance on external borrowings. This lower ratio signifies that the company has a more equity base relative to its debt, lowering financial risk.
The continuous execution and growth is a standout example of how strategic planning, diversified revenue streams, and a commitment to innovation can drive sustainable growth in the aviation sector. From its impressive core operations, handling millions of passengers, managing a high volume of flight movements, and continuously upgrading its infrastructure, to its financial performance characterized by record revenues and profitability, Cochin International Airport unlisted shares have gained confidence among investors. The airport’s ability to generate stable aeronautical income through regulated charges, combined with the dynamic and growing non-aeronautical revenue streams, positions it as a resilient and forward-thinking enterprise.